human evolution

The Incredible Journey of Human Evolution: Exploring Our Origins
Unveiling the Story of Human Evolution: Tracing Our Journey from Bacteria to Homo- sapiens
01-Mar-2023
Bio-Science
Last year, on my mother's birthday, I surprised her with a special gift—an Evolution Tree showcasing the path from the beginning of life to our species, Homo sapiens. Let's embark on this extraordinary adventure together!
The Organic Compounds which have the ability to make their replica are classified into two groups: Life and Virus. In this article we are discussing the Human Evolution Tree. So, we will start our journey through Life.
Life
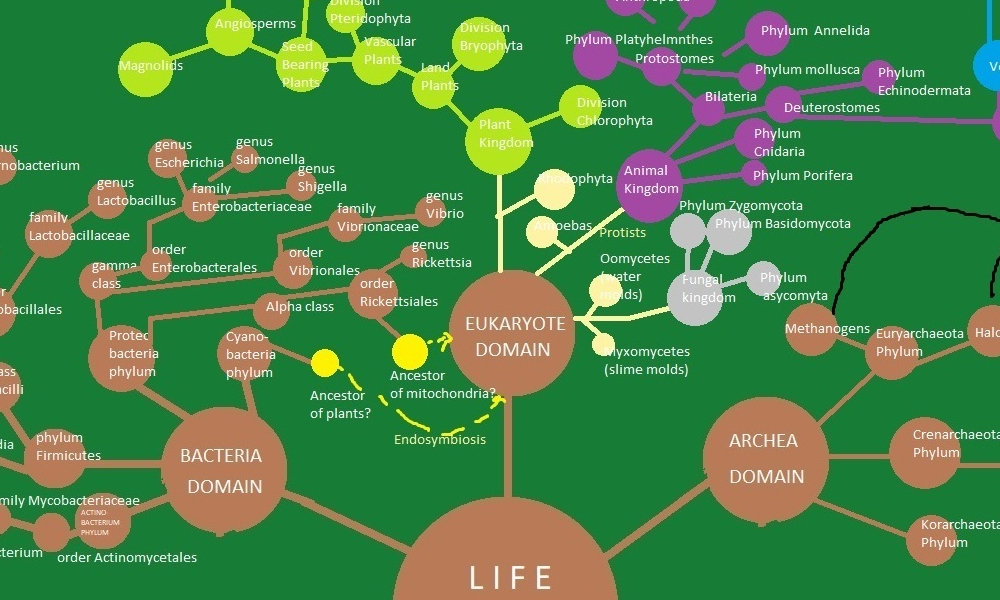
The journey of human evolution begins with the origin of life itself. Billions of years ago, life on Earth started as simple organisms, gradually evolving and diversifying over time. The life is further divided into three groups: Bacteria Domain, Eukaryote Domain and Archea Domain. We are Eukaryotes which evolved from Bacteria.
Bacteria Domain
We are only focusing on human evolution so let’s explore the pathway. The journey starts from the Alpha Class of Proteo Bacteria Phylum of the Bacteria Domain. It contains the order Rickettsiales which further contains the ancestor of Mitochondria which produced Mitochondria, the Organelle, in other bacteria by Endosymbiosis which made the very first Eukaryotes.
Eukaryote Domain
Eukaryotes are a type of organisms with complex cell structures. They include various life forms, such as plants, animals, fungi, and protists. Our journey starts in this diverse domain.
Animal Kingdom
Within the Eukaryote Domain, we find the Animal Kingdom. This kingdom encompasses a wide range of organisms, from tiny insects to majestic mammals.
Phylum Chordata
Chordata is a special group within the Animal Kingdom that includes animals with a notochord, a flexible rod-like structure. This group also includes vertebrates, which are animals with a backbone.
Vertebrates
Vertebrates are animals with a well-defined backbone or spinal column. They include fish, reptiles, birds, and mammals, which we humans belong to.
Class Sarcopterygii
Within the vertebrates, we find the class Sarcopterygii, which includes organisms with fleshy fin-like limbs. This group played a crucial role in the evolution of terrestrial animals.
Tetrapods
Tetrapods are a group of animals that have four limbs or descended from four-limbed ancestors. This group includes amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Amniotes
Amniotes are a group of tetrapods that have a specialized membrane called the amniotic sac. This adaptation allowed them to lay eggs on land, enabling further diversification.
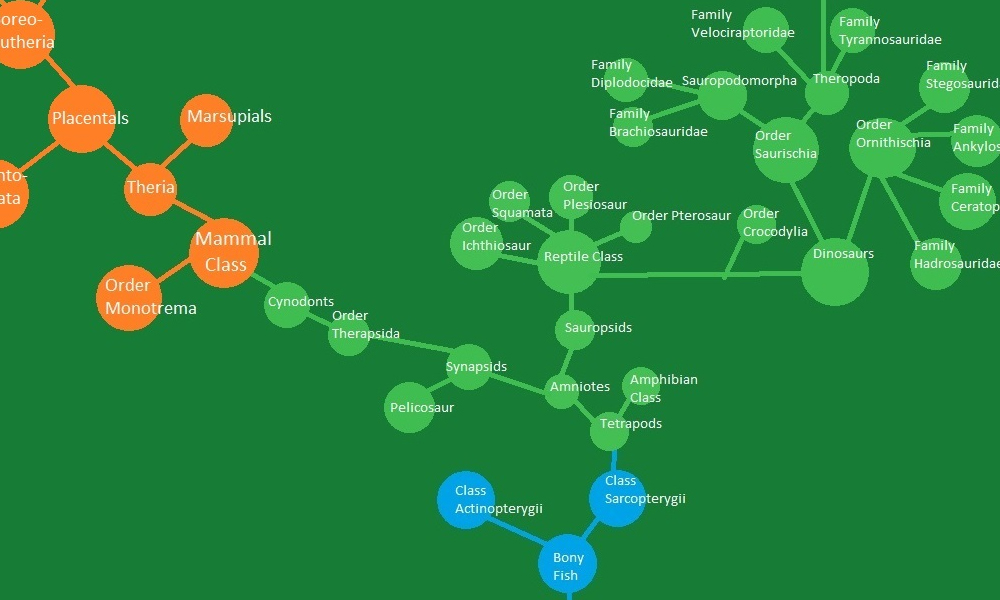
Mammals
Mammals are a fascinating group of amniotes. They possess mammary glands that produce milk to nourish their young. Our journey takes a significant leap forward with the emergence of mammals.
Placentals
Placentals are a subgroup of mammals that give birth to fully developed young. They nourish their offspring through a placenta, a remarkable adaptation that allowed for longer gestation periods and increased survival chances.
Boreo-eutheria
Boreo-eutheria is a group of placentals that includes various mammalian orders, such as primates, rodents, and carnivores. This diverse group set the stage for our primate ancestors.
Supra Primates
Supra Primates are primates that share common ancestry beyond prosimians, such as lemurs and tarsiers. This group includes monkeys, apes, and humans.
Apes
Apes are a family of primates that include gorillas, orangutans, chimpanzees, bonobos, and humans. We share a common ancestor with them, which brings us closer to our own species.
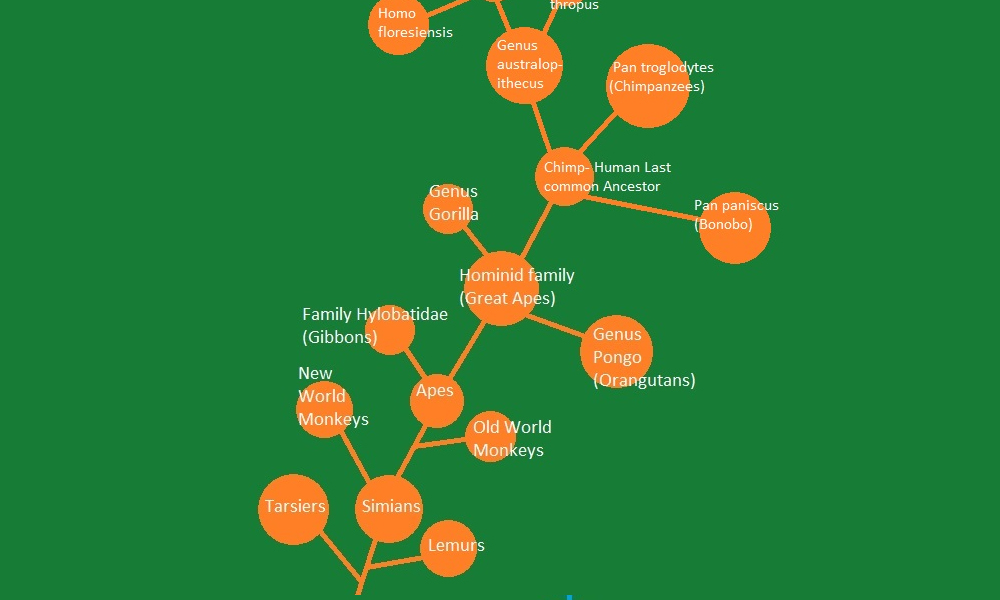
Hominid Family
The hominid family consists of our human ancestors and their close relatives. This group showcases the gradual development of human-like characteristics.
Chimp-Human Last Common Ancestor
The last common ancestor between chimpanzees and humans represents a significant milestone in our evolutionary history. From this point, our lineage branched off in different directions.
Genus Australopithecus
Australopithecus is a genus of early hominins that existed millions of years ago. They walked on two legs and possessed some human-like features.Genus Homo
Genus Homo includes various species within the human evolutionary lineage. Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo neanderthalensis are some notable examples.
Homo Ergaster
Homo ergaster is a species of early humans that lived in Africa around 1.9 million years ago. They displayed significant advancements in tool-making and were highly adaptable.
Homo Heidelbergensis
Homo heidelbergensis represents another important species in our evolutionary journey. They had larger brains and more sophisticated behaviors.
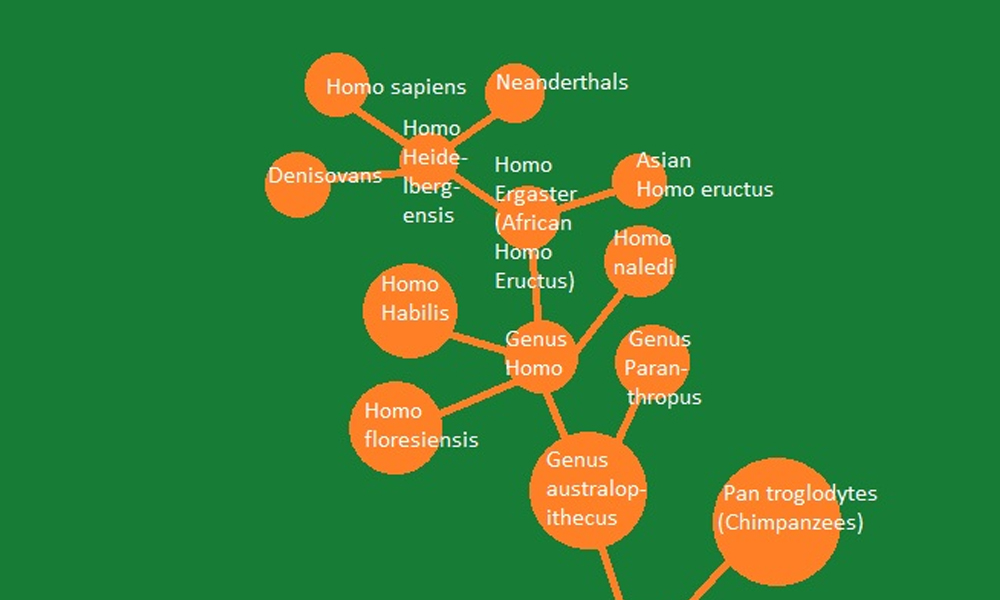
Homo Sapiens
Finally, we reach our own species, Homo sapiens, which means "wise human." We are the result of millions of years of evolution, with unique cognitive abilities and complex societies.
Conclusion
From the origin of life to the emergence of Homo sapiens, we witnessed the remarkable transformations that led to our existence.
© Emon's Lab 2023. All Rights Reserved. Designed by HTML Codex
